Fermentation of Soybean Meal to Improve Diet Formulation for Common Carp Cyprinus carpio L.
Keywords:
Fermented soybean meal, Feed formulation, Fish nutrition, Cyprinus carpio L.Abstract
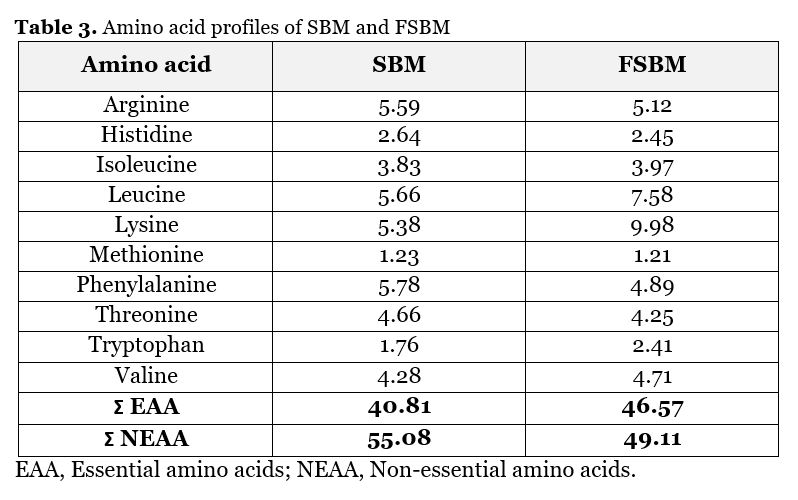
This investigation aimed to evaluate the chemo-biological fermentation of FSBM for partial substitution of SBM at ratios of (C 0%, T1 15%, T2 25%, and T3 35%) in diets formulated for common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) juveniles. The FSBM contained 51.22% protein and 17 amino acids in varying proportions, including 10 essential amino acids, with Lysine having the highest value of 9.98 µg/100 µg protein. Growth parameters of the experimental fish were monitored for 56 days during which they were fed at 3% of their live body weight. Fish were weighed biweekly to adjust feed ration. Results showed that diet T2 had the highest values for initial weight, final weight, weight gain, relative growth rate, SGR, FCR and PER with values of 14.7 g, 31.4 g, 16.7 g, 113.6 %, 1.355%/day, 1.91 and 1.603 respectively. Control diet (C) achieved the lowest values with rates of 15.1, 25.9, 10.8, 71.5, 0.963, 2.83 and 1.078, respectively, with significant difference (p≤0.05) in comparison with other treatments. The highest total apparent digestibility coefficient 79.6 % was recorded in treatment T2 (25% supplementation), and the lowest recorded 75.7% with no supplementation treatment (control). The same trend was observed for the digestibility of protein, fat, ash and carbohydrate. From the results of Statistical analysis significant differences (p≤0.05) were revealed between supplementation treatments (T1, T2, and T3) when compared with control, except for fat and ash digestibility, where all treatments showed non-significant differences (p≥0.05). The results indicated that FSBM supplemented treatments (T1, T2, and T3) achieved better growth than control, where T2 diet clearly outperforming the other dietary treatments in measured nutrition and growth parameters.
Metrics
References
Abdel-Aziz, M.; Bessat, M.; Fadel, A. and Elblehi, S. (2020). Responses of dietary supplementation of probiotic effective microorganisms (EMs) in Oreochromis niloticus on growth, hematological, intestinal histopathological, and antiparasitic activities, Aquacult. Int., 28, 947 – 963.
Abdel-Latif, H.M.; Shukry, M. and Abd-Elaziz, R.A. (2022). Clinico-pathological findings and expression of inflammatory cytokines, apoptosis, and oxidative stress-related genes draw mechanistic insights in Nile tilapia reared under Ammonia-N exposure and Aeromonas hydrophila challenge, Fish Shellfish Immunol., 127,1 -12.
Abdulkadir, M.; Abubakar, G.I. and Mohammed. A. (2010). Production and characterization of oil from fishes. ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci.,5, (7): 1 – 5.
AbdulKari, Z.A.; Kabir, M.A.; Mat, K.; Rusli, N.D.; Abdul Razab, M.K.A.; Ariff, N.S.N.A.; Edinur, H.A.; Abdul Rahim, M.Z.; Pati, S.; Dawood, M.A.O. and Wei, L.S. (2021). The possibility of replacing fish meal with fermented soy pulp on the growth performance, blood biochemistry, liver, and intestinal morphology of African catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Aquac. Rep., 21, (1 – 10) 100815.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aqrep.2021.100815.
Adeyemo, S.M. and Onilude, A.A. (2013). Enzymatic reduction of anti-nutritional factors in fermenting soybeans by Lactobacillus plantarum isolates from fermenting cereals, Niger. Niger. Food J. 31, (2): 84 – 90. doi:10.1016/S0189-7241(15)30080-1
Agboola, J.O.; Overland, M.; Skrede, A. and Hansen, J. O. (2021). Yeast as a major protein rich ingredient in aquafeeds: A review of the implications for aquaculture production. Rev. Aquac., 13, (2): 949 – 970.
Al-Kanaani, S.M.N. (2014). Utilization of fish silage fermented with date fruit residues for feeding the common carp Cyprinus carpio L. and its physiological and histological effects. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Basrah, Agricultural Sciences: 246pp.
Al-Noor, J.M.; Al-Tameemi, R.A. and Najim, S.M. (2023). Preparation of Fish Meal from Various Fishery Sources for Use in Young Common Carp Cyprinus carpio L. Diets, Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish., 27, (5): 959 – 972.
Al-Noor, J.M.; Najimi, S.M. and Al-Faiz, N.A. (2025). Extraction of gelatin from fish wastes for use in diets for the goldfish Carassius auratus. Iraqi J. Aquacult. 22, (1): 17 – 36.
AOAC. (2000). Official Methods of Analysis, 17th ed. Washington, DC: Association of Official Analytical Chemists.
Belewu, M.A. and Sam, R. (2010). Solid state fermentation of Jatropha curcas kernel cake: proximate composition and anti-nutritional components, J. Yeast Fungal Res., 1, 44 – 46.
Chinma, C. E.; Ilowefah, M. and Muhammad, K. (2014). Optimization of rice bran fermentation conditions enhanced by baker’s yeast for extraction of protein concentrate. Niger. Food J., 32, (1): 126 – 132.
Dai, C.; Ma, H.; He, R.; Huang, L.; Zhu, S. and Ding, Q. (2017). Improvement of nutritional value and bioactivity of soybean meal by solid-state fermentation with Bacillus subtilis. LWT – Food Sci. Technol., (86): 1 – 7.
DOI: 10.1016/j.lwt.2017.07.041.
El-Dakar, A.Y.; Elgamal, A.A.; Amer, M.A.; Mohammed, A.S. and Abdel-Aziz, M.F. (2023). Evaluation of fermented soybean meal by Bacillus subtilis as an alternative to fishmeal on the growth, and physiological status of Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus fingerlings. Heliyon, 9, (1 – 11) e19602.
FAO (2020). The state of world fisheries and aquaculture 2019. Rome: 28 p.
Ghaly, A. E.; Ramakrishnan, V. V.; Brooks, M. S.; Budge, S. M. and Dave, D. (2013). Fish processing wastes as a potential source of proteins, amino acids and oils: A Critical Review. J. Microb. Biochem. Technol., 5, (4): 107 – 129.
Guo, B.; Huang, L.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Huang, T.; Ma, L. and X Leng, X. (2023). Effects of Fermented Soybean Meal Substituting Plant Protein and Fish Meal on Growth, Flesh Quality, and Intestinal Microbiota of Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides). Aquac. Nutr. Article ID 6649754, 14 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2023/6649754.
Hamidoghli, A., Yun, H., Shahkar, E., Won, S., Hong, J., Bai, S.C. (2018). Optimum dietary protein-to-energy ratio for juvenile whiteleg shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei, reared in a biofloc system. Aquac. Res., 49, 1875 – 1886.
Hettiarachchy, N. S. (2018). Yeast fermentation of rice bran extracts. U.S. Patents Granted. 9,894,920. Board of Trustees of the University of Arkansas. Available at: https://patents.google.com/patent/US9894920B2/en
Hong, K.J.; Lee, C.H.; Kim, S.W. (2004). Aspergillus oryzae GB-107 fermentation improves nutritional quality of food soybeans and feed soybean meals. J. Med. Food., 7, 430 – 435.
Hortillosa, E.M.; Amar, M.J.A.; Nunal, S.N.; Pedroso, F.L. and Ferriols, V.M.E.N. (2022). Effects of putative dietary probiotics from the gut of milkfish (Chanos chanos) on the growth performance and intestinal enzymatic activities of juvenile Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquac., Res., 53, (1): 98 – 108. https://doi.org/10.1111/ are 15556.
Jassim, I.N.; Najim, S.M.; Al-Noor, J.M. (2024). Exploitation of Raw, Fermented and Microwave- Heated Rice Bran as Carbohydrate Alternatives in Young Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) Diets. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish., 28, (2): 217 – 234.
DOI:10.21608/ejabf.2024.346835.
Kalpanadevi, C.; Singh, V. and Subramanian, R. (2018). Influence of milling on the nutritional composition of bran from different rice varieties. J. Food Sci. Technol., 55, 2259 – 2269.
Li, C.; Tian, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, B. and Ma, Q. (2022). Effects of replacing fishmeal by raw or Lactobacillus acidophilus fermented soybean meal on growth, intestinal digestive and immune-related enzyme activities, morphology, and microbiota in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.). Aquac. Nutr., Article ID 2643235, 13 pages.
Li, C.; Zhang, B.; Liu, C.; Zhou, H.; Wang, X.; Mai, K. and He, G. (2020). Effects of dietary raw or Enterococcus faecium fermented soybean meal on growth, antioxidant status, intestinal microbiota, morphology, and inflammatory responses in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol., (100): 261 – 271.
DOI: 10.1016/j.fsi.2020.02.070.
Malik, W.A. and Javed, S. (2021). Biochemical characterization of cellulase from Bacillus subtilis strain and its effect on digestibility and structural modifications of lignocellulose rich biomass. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol., 9, 800265 https://doi.org/ 10.3389/fbioe.2021.800265.
Mukherjee, R.; Chakraborty, R. and Dutta, A. (2016). Role of fermentation in improving nutritional quality of soybean meal a review,” Asian-Australasian. J. Anim. Sci., 29, (11): 1523 – 1529.
Najim, S. M. and Al-Tameemi, R. A. (2023). The Evaluation of Bakery Waste as a Replacement for Corn Meal and Barley Flour in the Diets of the Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) Fingerlings. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish., 27, (2):709 – 721.
Nguyen, H.P.; Thuoc, D.V.; Thu, N.T.T.; Mai, H.T.T.; Hoa, N.T.K.; Nhi, N.T.T.; Thao, N.P.; Loan, T.T. and My, N.T.H. (2023). Effects of Dietary Replacement of Fish Meal by Raw and Fermented Soybean Residues on Growth Performance, Biological Parameters and Nutrient Digestibility in Red Tilapia Fish (Oreochromis sp.). Pakistan J. Zool., 55, (5): 2065 – 2074.
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.17582/journal.pjz/20211015111004.
Noaman, O.; Eid, A. and Elsayed, K. (2015). Effect of fermented soybean on growth performance of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus), J. Ani. Poul. Fish Prod., 3, (1): 31 – 37.
Olukomaiya, O.O.; Adiamo, O.Q.; Fernando, W.C.; Mereddy, R.; Li, X.; Sultanbawa, Y. (2020). Effect of solid-state fermentation on proximate composition, anti-nutritional factor, microbiological and functional properties of lupin flour. Food Chem., 315, 126238.
Osibona, A.O.; Kusemiju, K. and Akande, G.R. (2009). Fatty acid composition and amino acid profile of two freshwater species, African catfish (Clarias gariepinus) and tilapia (Tilapia zillii). Afr. J. Food Agric. Nutr. Dev., 9 (1): 608 – 621.
Phinyo, M.; Pumma, S.; Thinjan, P.; Wangkahart, E. and Soonthornchai, W. (2024). Effects of dietary fermented soybean meal with Thua nao starter on the growth performance, body composition, and disease resistance against Aeromonas hydrophila of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquac. Rep., 34, (1 – 10) 101890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aqrep.2023.101890.
Pi, X.; Sun, Y.; Deng, X.; Xin, D.; Cheng, J. and Guo, M. (2022). Characterization of the reduced IgE binding capacity in boiled and autoclaved soybeans through proteomic approaches. Foods, 11, (3): 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11030479.
Picoli, F.; Deolindo, G.L.; Serafini, S.; Alcantara Lopes, D.L.D.A. and Fabregat, T.E.P. (2024). Fermented soybean meal (FSFM) and Spirulina (Arthrospira platensis) biomass as potential substitutes for fishmeal for tilapia and other fish species cultivated in intensive systems. Rev. Ciênc. Agroveter., 23, (4): 705 – 722.
Pratiwy, F.M. and Triyani, D.A. (2022). Replacement of Fish Meal with Fermented Soybean Meal in Fish Feed: A Review. Asian J. Fish. Aqu. Res20, (6): 71 – 77. 2022; Article no. AJFAR.94720.
Qiu, Z.; Xu, Q.; Xie, D.; Zhao, J.; Yamamoto, F.Y.; Hong Xu, H. and Zhao, j. (2023). Effects of the replacement of dietary fish meal with poultry by-product meal on growth and intestinal health of Chinese soft-shelled turtle (Pelodiscus sinensis). Animals, 13, (5): 865.
Rhema, Z. A. and Al-Noor, J. M. (2022). Health and nutritional performance of young common carp Cyprinus carpio L. feeding diets with added bakery yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Int. J. Health Sci., 6, (S6): 2424 – 2437.
Rostika, R. and Safitri, R. (2012). Influence of fish feed containing corn-cob was fermented by Trichoderma sp, Aspergillus sp, Rhizopus Oligosporusto the rate of growth of java barb (Puntius gonionitus). APCBEE Procedia., (2):148 – 152. DOI: 10.1016/j.apcbee.2012.06.027.
Shapawi, R.; Ng, W.K. and Mustafa, S. (2007). Replacement of fish meal with poultry by-product meal in diets formulated for the humpback grouper, Cromilepte altivelis. Aquaculture, 273(1):118 – 126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2007.09.014.
Siddik, M.A.B.; Julien, B.B.; Islam, S.M.M. and Francis, D.S. (2024). Fermentation in aquafeed processing: Achieving sustainability in feeds for global aquaculture production. Rev Aquac., 16:1244 – 1265.
Tacon, A.G.J (1990). Standard methods for the nutrition and feeding of farmed fish and shrimp. In: Nutritive sources and composition, (2). argent Laboratories Press, Redmond, Washington, 129p.
Talbot, C. (1985). Laboratory methods in fish feeding and nutritional studies. In: Fish energetics: New perspectives. Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands: 125 – 154 pp.
Vidotti, R.M.; Viegas, E.M.M. and Carneiro, D.J. (2003). Amino acid composition of processed fish silage using different raw materials. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol., 105: 199 – 204.
Wang, Z.; Yang, M.; Wang, L.; Lu, K.; Song, K. and Zhang, C. (2021). Bacillus subtilis LCBS1 supplementation and replacement of fish meal with fermented soybean meal in bullfrog (Lithobates catesbeianus) diets: effects on growth performance, feed digestibility and gut health. Aquaculture. 545:737217. DOI: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2021.737217.
Weng, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhuang, W.; Yang, T.; Xu, X.; Liu, J.; Xu, Z., Chen, R.; Wang, Q.; Wang, S.; Cai, Y. and Ying, H. (2023). Effect of Replacing Fish Meal Using Fermented Soybean Meal on Growth Performance, Intestine Bacterial Diversity, and Key Gene Expression of Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides). Fermentation, 2023, 9, 520. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9060520.
Xu, C.; Liu, W.; Zhang, D.; Liu, J.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, C. and Chi, C. (2020). Effects of partial fish meal replacement with two fermented soybean meals on the growth of and protein metabolism in the Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis), Aquacult. Rep., 17, (2020), 100328.
Yang, H.; Bian, Y.; Huang, L.; Lan, Q.; Ma, L.; Li, X. and Leng, X. (2022). Effects of replacing fish meal with fermented soybean meal on the growth performance, intestinal microbiota, morphology and disease resistance of largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Aquac. Rep., 22, 100954
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aqrep.2021.100954.
Yaqub, A.Q.; Al-Noor, J.M. and Mojer, A.M. (2025). Utilization of Poultry Slaughterhouse Waste Silage as a Protein Source in Diets of the Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) Fingerlings. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish., 29, (1): 1047 – 1070.
DOI:10.21608/ejabf.2025.407764.
Zakaria, M.K; Abdul Kari, Z; Doan, H.V; Kabir, M.A; Harun, H.C; Sukri, S.A.M; Goh, K.W; Wee, W; Khoo, M.I. and Wei, L.S. (2022). Fermented Soybean Meal (FSBM) in African Catfish (Clarias gariepinus) Diets: Effects on Growth Performance, Fish Gut Microbiota Analysis, Blood Hematology, and Liver Morphology. Life 2022, 12, 1851. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12111851.
Zhang, Q; Guo, M; Li, F; Qin, M; Yang, Q; Yu, H; Xu, J; Liu, Y. and Tong, T. (2023). Evaluation of Fermented Soybean Meal to Replace a Portion Fish Meal on Growth Performance, Antioxidant Capacity, Immunity, and mTOR Signaling Pathway of Coho Salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch). Aquac. Nutr., 2023, Article ID 2558173, 13 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2023/2558173.
Zhao, M; Yu, D; Liu, Q; Ma, S; Xu, J. and Yu, J. (2022). Co-fermentation of Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus licheniformis and its application in the feeding of Koi. Aquac. Res., 53, (17): 6056 – 6068. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.16077.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2026 Iraqi Journal of Aquaculture

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.






