Comparative Evaluation of Algae, Yeast, and Mixed Diets on Growth Performance and Proximate Composition of Artemia franciscana in a 30-Day Culture System
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.58629/ijaq.v22i2.741Keywords:
Artemia nauplii, Chlorella vulgaris, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Growth performance, Proximate composition.Abstract
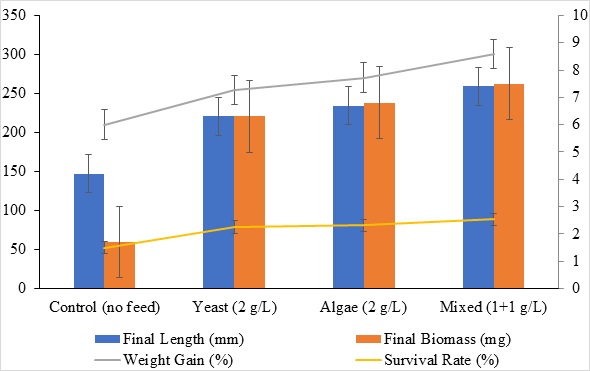
This study investigated the effects of dietary supplementation with microalgae (Chlorella vulgaris), yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae), and a 1:1 combination of both on the growth performance and proximate composition of Artemia franciscana over a 30-day culture period. Four feeding treatments were evaluated: a control (natural seawater microbial load), yeast-only (2 g/L), algae-only (2 g/L), and a mixed diet (1 g/L yeast + 1 g/L algae). The results revealed that dietary treatment significantly influenced all measured parameters (p ≤ 0.05). The mixed diet group achieved the highest growth performance, with a final length of 7.4 ± 0.4 mm, biomass of 7.5 ± 0.3 mg, weight gain of 300.5 ± 9.6%, and survival rate of 88.4 ± 2.6%. Algae-fed Artemia also showed notable improvement (final length: 6.7 ± 0.5 mm; biomass: 6.8 ± 0.4 mg; weight gain: 270.3 ± 11.2%; survival: 81.1 ± 2.3%), followed by the yeast group (final length: 6.3 ± 0.3 mm; biomass: 6.3 ± 0.3 mg; weight gain: 254.5 ± 10.6%; survival: 78.7 ± 2.7%). The control group recorded the lowest values across all metrics, with a final biomass of 1.7 ± 0.1 mg and survival of 52.4 ± 3.5%. Proximate composition analysis further confirmed the nutritional benefits of the mixed diet, which produced the highest crude protein (53.7 ± 1.2%) and lipid content (15.4 ± 0.3%) with reduced ash (11.3 ± 0.6%) and moisture levels (75.3 ± 0.5%). These findings demonstrate that a combined yeast–algae diet provides complementary nutrients that enhance Artemia growth and nutritional quality. These results highlight the potential of mixed yeast–algae diets as a sustainable and cost-effective strategy for producing nutritionally enriched Artemia in aquaculture systems.
Metrics
References
Al Bassam, N. H., Shakir, H. F. and Taha, A. H. (2023). Effect of poultry waste powder supplemented with papain, phytase, and pepsin enzymes on digestion and growth of common carp, Cyprinus carpio L. Iranian Journal of Ichthyology, 9(3): 175–179.
Abreu, J.L.D., Campos, C.V.F.D.S., Lima, P.C.M.D., Brandão, B.D.C.S., Mota, G.C.P., Moraes, L.B.S.D. and Gálvez, A.O. (2025). Effect of the Chlorella vulgaris Bioencapsulated by Daphnia magna on the Growth and Nutritional Value of the Penaeus vannamei Cultured in a Synbiotic System. MDPI, Sustainability, 17(10): 4674.
Al Sulivany B.S.A., Owais, M., Dernekbaş, S., Fazal, R.M., Selamoglu, Z. and Shahid, A. (2025). Salinity and Organic Feed Optimization for Artemia franciscana Culture: Differential Survival Responses to Chlorella vulgaris and Saccharomyces cerevisiae in Nauplii and Adults. Iraqi Journal of Aquaculture, 22(1): 95–110.
Al Sulivany, B., Owais, M., Fazal, R., Asad, F., Hussein, N., and Selamoglu, Z. (2024). Seasonal effects of protein levels on common carp (Cyprinus carpio) body composition. Iraqi Journal of Aquaculture, 21(2): 111–127.
Al-Sahlany, S.T.G., Niamah, A.K., Verma, D.K., Prabhakar, P., Patel, A.R., Thakur, M., and Singh, S. (2025). Applications of Green Synthesis of Nanoparticles Using Microorganisms in Food and Dairy Products. Processes, 13(5): 1560.
Anand, P.S., Aravind, R., Balasubramanian, C.P., Dayal, J.S., Kumar, S., Rajan, R.V. and Vijayan, K.K. (2024). Artemia biomass: A functional live maturation feed for Indian white shrimp, Penaeus indicus broodstock, and its culture prospective under diverse management regime. Aquaculture, 588, 740851.
Andrade-Bustamante, G., Martínez-Ruiz, F.E., Ortega-García, J., Renganathan, P., Gaysina, L.A., Mahendhiran, M. and Puente, E. O. R. (2025). Microalgae-Based Functional Foods: A Blue-Green Revolution in Sustainable Nutrition and Health. Applied Microbiology, 5(2): 1-32.
AOAC (1990). Official Methods of Analysis (15th ed.). Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Arlington, VA.
Asem, A., Rogers, D.C., Gajardo, G., Hontoria, F., and Sorgeloos, P. (1995). Artemia tunisiana Bowen and Sterling, 1978 (Anostraca: Artemiina: Artemiidae) is a nomen dubium. Journal of Crustacean Biology, 45(2): ruaf019.
Bakshi, S., Kanetkar, P., Bunkar, D. S., Browne, C. and Paswan, V. K. (2025). Chlorella sp. as a promising protein source: insight to novel extraction techniques, nutritional and techno-functional attributes of derived proteins. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 1-29.
Chen, H., Yu, S., Yu, Z., Ma, M., Liu, M., and Pei, H. (2024). Phycoremediation Potential of Salt-Tolerant Microalgal Species: Motion, Metabolic Characteristics, and Their Application for Saline-Alkali Soil Improvement in Eco-Farms. MDP, IMicroorganisms, 12(4): 676.
Dinesh, R., Nandhakumar, S., Anand, C., Kumar, J., and Padmavathy, P. (2025). Comparative analysis of Nannochloropsis oculata, Dunaliella salina, and Tetraselmis gracilis as feed sources for rotifer, Brachionus plicatilis: Effects on population dynamics, biochemical composition, and fatty acid profile. Journal of Applied Phycology, 37(2): 1029-1039.
Dutta, S., Sarkar, R., Saha, N., Suthar, M.K., Gawdiya, S., Roy Choudhury, M. and Das, S. (2025). Beyond nutrition: a two-decade systematic review of the ethnopharmacological potential and therapeutic promise of Amaranthus sp. Phytochemistry Reviews, 1-33.
Glencross, B. D., Bachis, E., Betancor, M.B., Calder, P., Liland, N., Newton, R. and Ruyter, B. (2025). Omega-3 futures in aquaculture: exploring the supply and demands for long-chain Omega-3 essential fatty acids by aquaculture species. Reviews in Fisheries Science & Aquaculture, 33(2): 167-216.
Haris, D. I., Yaminudin, J., Othman, S. H., Lim, K. C., Ismail, I., Wulan Sari, P. D. and Karim, M. (2024). The use of commercial feed and microdiets incorporated with probiotics in Penaeid shrimp culture: a short review. Latin american journal of aquatic research, 52(3): 350-367.
Ilieva, Y., Zaharieva, M.M., Kroumov, A.D. and Najdenski, H. (2024). Antimicrobial and Ecological Potential of Chlorellaceae and Scenedesmaceae with a Focus on Wastewater Treatment and Industry. Fermentation, 10(7): 341.
Jacob, A.T., Kapinga, I.B., Mwijage, A.P., Luvanga, A., Mremi, A., Sekadende, C. and Matondo, A. B. (2025). Biometry, hatching efficiency, growth performance and survival of the brine shrimp Artemia franciscana from Tanzania. African Journal of Marine Science, 47(1): 31-37.
Khanzadeh, M., Hoseinifar, S.H., Yazici, M. and Van Doan, H. (2025). Fermentation of Sargassum ilicifolium with Probiotics (Lactobacillus plantarum and Saccharomyces cerevisiae) Enhances Growth, Immunity, and Gene Expression in Rainbow Trout Before and After Challenge with Streptococcus iniae. Probiotics and Antimicrobial Proteins, 1-25.
Kour, D., Rana, K.L., Yadav, N., Yadav, A.N., Singh, J., Rastegari, A.A. and Saxena, A.K. (2019). Agriculturally and industrially important fungi: current developments and potential biotechnological applications. Recent advancement in white biotechnology through fungi: Volume 2: Perspective for value-added products and environments, 1-64.
Kim, N., Ahn, Y., Ko, K., Kim, B., Han, K., Suh, H.J., Jung, J. and Hong, K.B. (2023). Yeast Hydrolysate Inhibits Lipid Accumulation via Regulation of Lipid Accumulation-Related Genes in a Drosophila Model of High-Sugar Diet-Induced Obesity. International journal of molecular sciences, 24(22): 16302.
Liang, Q., Luan, Y., Wang, Z., Niu, J., Li, Y., Tang, H. and Liu, G. (2025). Integration of Biofloc and Ozone Nanobubbles for Enhanced Pathogen Control in Prenursery of Pacific White Shrimp (Penaeus vannamei). MDPI, Fishes, 10(5): 218.
Lopes, D., Rey, F., Gomes, A., Duarte, L., Pereira, J., Pinho, M. and Domingues, R. (2024). Tracing the impact of domestic storage conditions on antioxidant activity and lipid profiles in the edible microalgae Chlorella vulgaris and Tetraselmis chui. Marine Drugs, 22(6): 254.
Manoharan, L., Suparmaniam, U., Lam, M.K., Chai, Y.H., Loy, A. C.M., Tan, I.S. and Lim, S. (2025). Advances in attached growth microalgae cultivation for third-generation biofuel production: opportunities, challenges, and future prospect. Brazilian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 1-36.
Marumure, J., Gwenzi, W., Makuvara, Z., Simbanegavi, T.T., Alufasi, R., Goredema, M. and Halabowski, D. (2025). Global Occurrence of Cyanotoxins in Drinking Water Systems: Recent Advances, Human Health Risks, Mitigation, and Future Directions. MDPI, Life, 15(5): 825.
Mendes, A. R., Spínola, M. P., Lordelo, M. and Prates, J. A. (2024). Chemical Compounds, Bioactivities, and Applications of Chlorella vulgaris in Food, Feed and Medicine. Journal of Applied Sciences, 14(23): 10810.
Mohamad Hassan, S., Albassam, N.H., Madlul, N.S. and Mahmood, A.S. (2024). Influence of different salinity concentrations on water quality and subsequent effects on hatchability rate of Artemia salina eggs. AIP Conf. Proc. 11, 3079 (1): 020007.
Mohamad Hassan, S, Salah, M, Albassam, N.H, Mdloul, N.S., Muhaimeed, A.R. and Sulaiman, M.A. (2025). Using the Diverse Vegetables as a Filtration plant in Aquaculture Intensive System. Tikrit Journal for Agricultural Sciences, 25(1): 1-16. doi: 10.25130/tjas.25.1.1
Owais M., Al Sulivany B.S.A., Bayan, M.S. and Fazal R.M. (2024). The Pangas Catfish Pangasius pangasius; Growth Efficiency and Nutritional Composition Under Variety of Saltwater Challenges. Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Biology and Fisheries, 28(6): 1-13. doi: 10.21608/ejabf.2024.389994
Panahi, Y., Khosroushahi, A.Y., Sahebkar, A., and Heidari, H.R. (2019). Impact of cultivation condition and media content onChlorella vulgaris composition. Advanced pharmaceutical bulletin, 9(2): 182.
Sánchez-Bayo, A., Morales, V., Rodríguez, R., Vicente, G. and Bautista, L.F. (2020). Cultivation of microalgae and cyanobacteria: Effect of operating conditions on growth and biomass composition. MDPI, Molecules, 25(12): 2834.
Santos, R.F.B., Godoy, A.C., Fantini-Hoag, L., Gomes, S.F., Moraes, L.B.S.D., Cahú, T.B. and Bezerra, R.D.S. (2025). Artemia biomass protein hydrolysate as a new feed for aquaculture: Litopenaeus vannamei (Mysis) performance. Aquaculture International, 33(4): 250.
Sharma, P., Saha, S., Chatterjee, S., Mandal, A.H., Ghosh, S., Saha, N.C. and Faggio, C. (2025). Toxicological and physiological impact and bioremediation strategies for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Chemistry and Ecology, 13(3): 1-24.
Sivamurugan, V., Murugesan, S. and Shanthi, N. (2025). Physiological Ecology of Soil Algae. In Soil Algae: Morphology, Ecology and Biotechnological Applications 4(2):117-149.
Sohel, A., Sahu, S., Mitchell, G. R. and Patel, M. K. (2025). 3D Food Printing: A Comprehensive Review and Critical Analysis On Technologies, Food Materials, Applications, Challenges, And Future Prospects. Food Engineering Reviews, 12(17): 1-29.
Wichaphian, A., Kamngoen, A., Pathom-Aree, W., Maneechote, W., Khuendee, T., Chromkaew, Y. and Srinuanpan, S. (2025). Integrating Microalgal Chlorella Biomass and Biorefinery Residues into Sustainable Agriculture and Food Production: Insights from Lettuce Cultivation. MDPI, Foods, 14(5): 808.
Yuslan, A., Suhaimi, H., Ghaffar, M.A., and Rasdi, N.W. (2025). Interactive effect of temperature and nitrogen concentrations on the growth, biochemical composition, and fatty acid profiles in freshwater microalgae, Chlorella sorokiniana and Scenedesmus quadricauda. Journal of Applied Phycology, 37, 1679–1702.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Iraqi Journal of Aquaculture

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.










