Molecular taxonomic reassessment and phylogenetic relationships of Middle Eastern Cyprinidae inferred from mitochondrial COX1 sequences retrieved from GenBank
Keywords:
Cyprinidae, COX1, DNA barcoding, Phylogenetic relationships, Taxonomic reassessment, Middle East, GenBank.Abstract
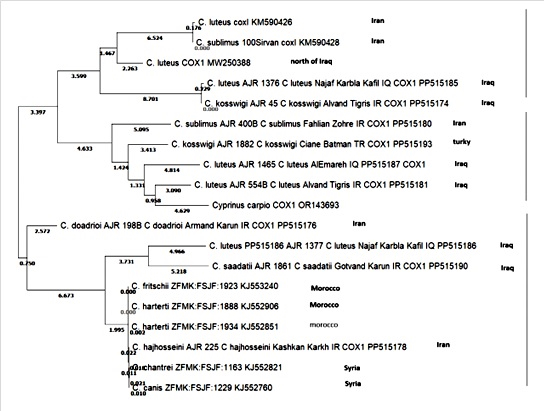
Cyprinidae is the most diverse and taxonomically challenging group of freshwater fish in the Middle East, where species identification is difficult due to morphological similarity and taxonomic instability. This paper presents a molecular taxonomic review and phylogenetic analysis of Middle Eastern cyprinids based on mitochondrial COX1 gene sequences downloaded from GenBank. A large dataset of publicly available COX1 sequences from various cyprinid genera and locations across the Middle East was assembled and analyzed. Alignment and genetic distances were calculated, and phylogenetic relationships were analyzed using Neighbor-Joining (NJ) and Minimum Evolution with bootstrap validation. The resulting phylogenetic trees revealed well-defined clades corresponding to recognized taxonomic groups, but also uncertainty in species delimitation and unpredictable clustering among closely related taxa. Although based on a single mitochondrial marker, the data demonstrate COX1's utility in resolving species-level relationships and provide initial insights into shallow phylogeographical structuring among Middle Eastern cyprinids. These patterns suggest potential taxonomic confusion and highlight the importance of integrative analyses incorporating other markers and morphological data. This study provides a molecular framework for elucidating cyprinid systematics in the Middle East and serves as a foundation for future evolutionary and systematic research.
Metrics
References
April, J.; Mayden, R.L.; Hanner, R.H. and Bernatchez, L. (2011). Genetic calibration of species diversity among North America’s freshwater fishes. Mol. Ecol. Resour., 11(4): 777–792. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-0998.2011.03019.x
Avise, J.C. (2000). Phylogeography: The History and Formation of Species. Harvard Univ. Press, Cambridge.
Bănărescu, P. (1992). Zoogeography of Fresh Waters, Vol. 2. Aula-Verlag, Wiesbaden. Dayrat, B. (2005). Towards integrative taxonomy. Trends Ecol. Evol., 20(9): 407-415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2005.05.020
Geiger, M.F.; Herder, F.; Monaghan, M.T.; Almada, V.; Barbieri, R.; Bariche, M.; Berrebi, P.; Bohlen, J.; Casal-López, M., and Delmastro, G.B., (2014). Spatial heterogeneity in the Mediterranean biodiversity hotspot affects barcoding accuracy of its freshwater fishes. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol., 75, 121–132.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2014.02.013
Harris, D.J. (2003). Can you bank on GenBank? Trends Ecol. Evol., 18(7), 317–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-5347(03)00119-2
He, S.; Mayden, R.L.; Wang, X.; Wang, W., and Tang, K.L. (2008). Molecular phylogenetics of the family Cyprinidae (Teleostei: Cypriniformes). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol., 49(3), 708–718. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2008.09.005
Hebert, P.D.N.; Cywinska, A.; Ball, S.L., and deWaard, J.R. (2003). Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proc. R. Soc. B, 270 (1512): 313–321.
https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2002.2218
Hubert, N.; Hanner, R.; Holm, E.; Mandrak, N.E.; Taylor, E.; Burridge, M.; Watkinson, D.; Dumont, P.; Curry, A., and Bentzen, P. (2008). Identifying Canadian freshwater fishes through DNA barcodes. PLoS ONE, 3(6): e2490.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0002490
Levin, B.A.; Freyhof, J.; Lajbner, Z.; Perea, S.; Abdoli, A.; Gaffaroğlu, M.; Özuluğ, M.; Rubenyan, H.R., and Salnikov, V.B. (2012). Phylogenetic relationships and biogeography of the genus Capoeta (Cyprinidae). J. Biogeogr., 39(6), 1106–1121. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2699.2012.02683.x
Nilsson, R.H.; Kristiansson, E.; Ryberg, M.; Hallenberg, N., and Larsson, K.H. (2006). Intraspecific ITS variability in the kingdom Fungi. Mol. Ecol., 15(5), 1287–1295. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2006.02842.x
Pante, E.; Schoelinck, C., and Puillandre, N. (2015). From integrative taxonomy to species description: one step beyond. Syst. Biol., 64(1): 152–160.
https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/syu083
Perea, S.; Böhme, M.; Zupančič, P.; Freyhof, J.; Šanda, R.; Özuluğ, M.; Abdoli, A., and Doadrio, I. (2010). Phylogenetic relationships and biogeographical patterns in Circum-Mediterranean Leuciscinae (Cyprinidae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol., 55(3): 1153–1164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2010.02.030
Ratnasingham, S. and Hebert, P.D.N. (2007). BOLD: The Barcode of Life Data System. Mol. Ecol. Notes, 7(3): 355–364. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-8286.2007.01678.x
Ward, R.D.; Zemlak, T.S.; Innes, B.H.; Last, P.R. and Hebert, P.D.N. (2005). DNA barcoding Australia’s fish species. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B, 360(1462): 1847–1857.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2026 Iraqi Journal of Aquaculture

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.






