Acute Toxicity and Behavioral Alterations as Biomarkers of Triclosan Exposure in Blue Tilapia Oreochromis aureus (Steindachner, 1864)
Keywords:
Triclosan, Oreochromis aureus, toxicity, behavioralAbstract
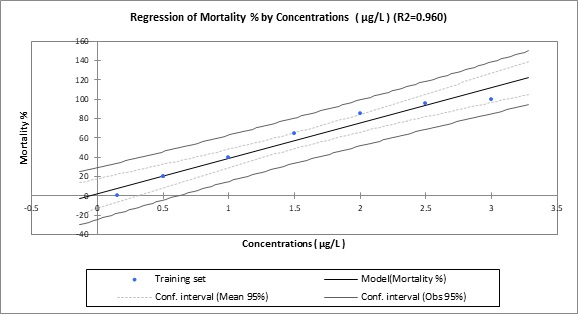
Several behavioral changes were observed in blue tilapia upon exposure to triclosan for 96 hours. The severity of these behavioral changes increased with concentration. Fish exhibited rapid swimming, rapid fin movements, abnormal operculum movements, attempts to ascend, and vertical jumps towards the water surface. They also showed loss of balance, respiratory distress, and capsizing. Over 96 hours of exposure, triclosan exhibited concentration-dependent toxicity, resulting in a progressive, proportional increase in fish mortality. Neither the control treatment nor the 0.15 µg/L treatment showed any mortality. However, at higher concentrations, 20% of fish in the 0.5 µg/L treatment, 40% in the 1 µg/L treatment, and 65% in the 1.5 µg/L treatment died. Increasing the triclosan concentration to 2 µg/L resulted in 85% mortality. The highest mortality rate (100%) was recorded in the 3 µg/L treatment.
Metrics
References
Allmyr, M.; Harden, F.; Toms, L.M.L.; Mueller, J.F.; McLachlan, M.S.; Adolfsson-Erici, M. and Sandborgh-Englund, G. (2008). The influence of age and gender on triclosan concentrations in Australian human blood serum. Sci. Total Environ., 393 (1): 162–167.
Hemalatha, D.; Nataraj, B.; Rangasamy, B.; Shobana, C. and Ramesh, M. (2019). DNA damage and physiological responses in an Indian major carp Labeo rohita exposed to an antimicrobial agent triclosan. Fish Physiol. Biochem., 45(4): 1463-1484.
Schultz, M.M.; Bartell, S.E. and Schoenfuss, H.L. (2012). Effects of triclosan and triclocarban, two ubiquitous environmental contaminants, on anatomy, physiology, and behavior of the fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas).Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 63(1): 114-124
Adolfsson-Erici, M.; Pettersson, M.; Parkkonen, J. and Sturve, J. (2002). Triclosan, a commonly used bactericide found in human milk and in the aquatic environment in Sweden. Chemosphere., 46(9-10): 1485-1489.
Arman, S. (2021). Effects of acute triclosan exposure on gill and liver tissues of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Ann Limnol-int. J. Limnol.,(Vol. 57: p. 6). EDP Sciences.
Capkin, E.; Ozcelep, T.; Kayis, S. and Altinok, I. (2017). Antimicrobial agents, triclosan, chloroxylenol, methylisothiazolinone and borax, used in cleaning had genotoxic and histopathologic effects on rainbow trout. Chemosphere., 182: 720-729.
Celebi, H. and Gok, O. (2018). Effect of triclosan exposure on mortality and behavioral changes of Poecilia reticulata and Danio rerio. Hum. Ecolo.l Risk Assess: Inter. J., 24(5): 1327-1341.
Dann, A. B. and Hontela, A. (2011). Triclosan: environmental exposure, toxicity and mechanisms of action. J. App.toxicol., 31(4): 285-311.
Deepika, S.; Padmavathy, P.; Srinivasan, A.; Sugumar, G. and Jawahar, P. (2021). Effect of triclosan (TCS) on the protein content and associated histological changes on tilapia, Oreochromis mossambicus (Peters, 1852). Enviro. Sci. Pollu. Res., 28(42): 59899-59907.
Drummond, R.A. and Russom, C.L. (1990). Behavioral toxicity syndromes: a promising tool for assessing toxicity mechanisms in juvenile fathead minnows. Enviro.Toxicol. chem., 9 (1): 37–46.
Fritsch, E. B.; Connon, R. E.; Werner, I.; Davies, R. E.; Beggel, S.; Feng, W. and Pessah, I. N. (2013). Triclosan impairs swimming behavior and alters expression of excitation-contraction coupling proteins in fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas). Enviro.sci. technol., 47(4): 2008-2017.
Gruber, S.J. and Munn, M.D. (1998). Organophosphate and carbamate insecticides in agricultural waters and cholinesterase (ChE) inhibition in common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Arch. Environ.Contam. Toxicol., 35(3): 391-396.
Heras, H.; Ackman, R.G. and Macpherson, E.J. (1992). Tainting of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) by petroleum hydrocarbons during a short-term exposure. Mar. Pollut. Bull., 24(6): 310-315.
Little, E.E. and Brewer, S.K. (2001). Neurobehavioral toxicity in fish. Target organ toxicity in marine and freshwater teleosts, 141-176.
Melvin, S.D.; Buck, D.R. and Fabbro, L.D. (2016). Diurnal activity patterns as a sensitive behavioural outcome in fish: effect of short‐term exposure to treated sewage and a sub‐lethal PPCP mixture. J. App.Toxico., 36(9): 1173-1182.
Nassef, M.; Matsumoto, S.; Seki, M.; Kang, I. J.; Moroishi, J.; Shimasaki, Y. and Oshima, Y. (2009). Pharmaceuticals and personal care products toxicity to Japanese medaka fish (Oryzias latipes). J. Fac. Agr., Kyushu Univ., 54(2): 407–411
Nassef, M.; Matsumoto, S.; Seki, M.; Khalil, F.; Kang, I. J.; Shimasaki, Y.; Oshima, Y.and Honjo, T. (2010). Acute effects of triclosan, diclofenac and carbamazepine on feeding performance of Japanese medaka fish (Oryzias latipes). Chemosphere, 80(9): 1095-1100.
Oliveira, R.; Domingues, I.; Koppe Grisolia, C. and Soares, A.M. (2009). Effects of triclosan on zebrafish early-life stages and adults. Enviro. Sci. Pollut. Res., 16(6): 679-688.
Orvos, D.R.; Versteeg, D.J.; Inauen, J.; Capdevielle, M.; Rothenstein, A. and Cunningham, V. (2002). Aquatic toxicity of triclosan. Enviro. Toxicol. Chem., 21(7): 1338-1349.
Priyatha, C.V. and Chitra, K.C. (2018). Acute toxicity of triclosan on the native freshwater fish, Anabas testudineus (Bloch, 1792): behavioral alterations and histopathological lesions. Int. J. Life Sci., 6(1): 166-172.
Rice, S.D.; Short, J.W.; Heintz, R.A.; Carls, M.G. and Moles, A. (2000). Life-history consequences of oil pollution in fish natal habitat. Energy, 1210-1215.
Sandahl, J.F.; Baldwin, D.H.; Jenkins, J.J. and Scholz, N.L. (2005). Comparative thresholds for acetylcholinesterase inhibition and behavioral impairment in coho salmon exposed to chlorpyrifos. Enviro. Toxicol. Chem., 24(1): 136-145.
Scott, G.R. and Sloman, K.A. (2004). The effects of environmental pollutants on complex fish behaviour: integrating behavioural and physiological indicators of toxicity. Aquat.toxicol., 68(4): 369-392.
Seenivasan, D.; Pandurengan, P.; Srinivasan, A.; Gopalrajan, S. and Paulraj, J. (2023). Short term effects of antimicrobial agent triclosan on Oreochromis mossambicus (Peters, 1852): Biochemical and genetic alterations. Indian. J. Anim. Res., 57(6): 788-794.
Song, X.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Yan, X.; Liang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Huang, L. and Zeng, H. (2021). Histopathology and transcriptome reveals the tissue-specific hepatotoxicity and gills injury in mosquitofish (Gambusia affinis) induced by sublethal concentration of triclosan. Ecotoxicol. Nviron. Saf., 220: 112325.
Vijitha, C.K.; Asifa, K.P. and Chitra, K.C. (2017). Assessment of genotoxic and haematological consequence of triclosan in the fish, Oreochromis niloticus (Linnaeus, 1758). Int.J. Appl. Res., 3(2): 101-109.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2026 Iraqi Journal of Aquaculture

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.






